Custom thermoforming is a powerful and cost-effective manufacturing process that enables the production of high-quality, durable plastic components for industries such as medical, aerospace, mass transit, automotive, and industrial equipment. Unlike injection molding, which requires expensive tooling, custom thermoforming offers faster production times, lower tooling costs, and greater flexibility in material selection and part size.
For engineers and designers, understanding the best practices of custom thermoforming is essential to creating optimized, manufacturable, and cost-efficient parts. In this guide, we’ll cover key design tips and tricks to enhance part performance, streamline manufacturing, and ensure consistent quality in your thermoformed products.
Understanding Custom Thermoforming and Its Advantages
What is Custom Thermoforming?
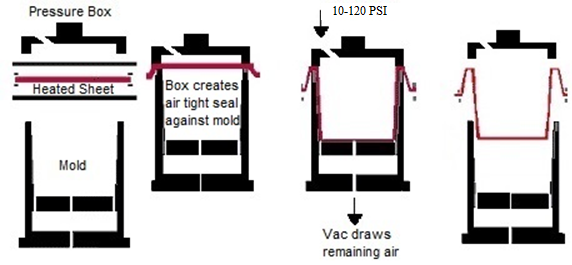
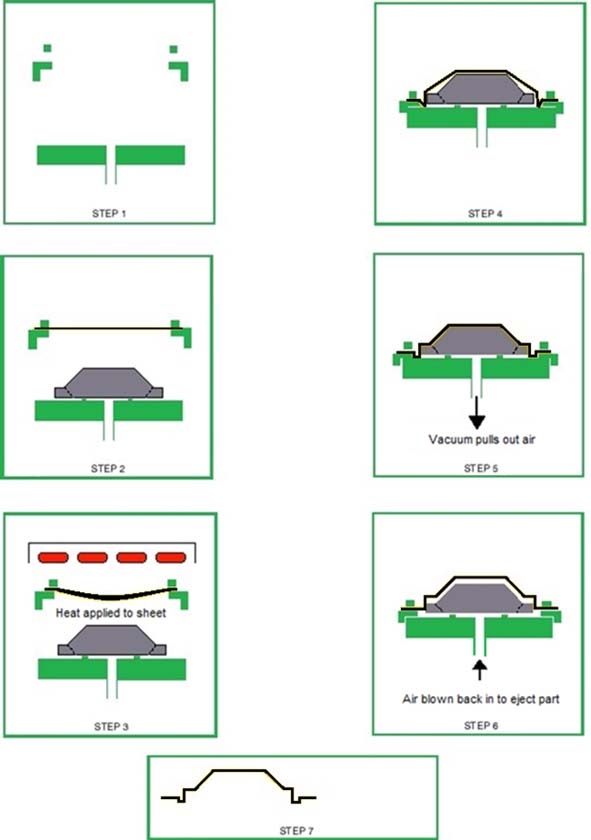
Custom thermoforming is a plastic molding process where thermoplastic sheets are heated until pliable and then shaped using a mold. The two primary types of thermoforming used in manufacturing are:
- Vacuum Forming – Uses vacuum pressure to draw the plastic sheet against a mold. Best for simple geometries and shallow draw depths.
- Pressure Forming – Uses both vacuum and compressed air to push the heated sheet into the mold. This allows for more complex designs, sharper details, and tighter tolerances.
Why Choose Custom Thermoforming?
Compared to other plastic molding processes, custom thermoforming offers:
✅ Lower Tooling Costs – Thermoforming molds are less expensive than injection molds, making it ideal for small to medium production runs.
✅ Faster Turnaround Times – Custom thermoformed parts can be designed, prototyped, and produced more quickly than parts made via other molding methods.
✅ Design Flexibility – Engineers can work with a wide range of materials, surface textures, colors, and thicknesses to meet application requirements.
✅ Large Part Capabilities – Unlike injection molding, thermoforming allows for large-scale parts with intricate designs.
Best Practices for Custom Thermoforming Design
Material Selection Matters
Choosing the right thermoplastic is critical to achieving optimal performance in your thermoformed parts. Key material considerations include:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): High impact resistance, cost-effective, excellent for enclosures and automotive components.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Exceptional strength and heat resistance, used for medical device covers and industrial applications.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Good chemical resistance, ideal for medical trays and packaging.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Chemical and moisture-resistant, used in industrial storage applications.
Pro Tip: Work with a thermoforming expert like CW Thomas to select the best material based on mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and end-use requirements.
Designing for Thermoforming: Key Considerations
Unlike injection molding, thermoforming requires specific design adjustments to ensure part quality and consistency.
✅ Draft Angles:
- Always include a minimum of 3° draft angle on vertical walls to allow for easy part release from the mold.
- For deep-draw parts, increase the draft angle to 5° or more.
✅ Wall Thickness Uniformity:
- Maintain a consistent wall thickness to avoid weak points and ensure structural integrity.
- Consider using reinforcing ribs or strategic material distribution to improve strength.
✅ Undercuts and Parting Lines:
- Avoid excessive undercuts, as they increase mold complexity and production time.
- If undercuts are necessary, consider secondary trimming to remove excess material.
✅ Radii and Corner Transitions:
- Use a minimum 0.125-inch radius on internal and external corners to reduce stress concentrations.
- Sharp corners can cause material thinning, leading to weak spots in the final product.
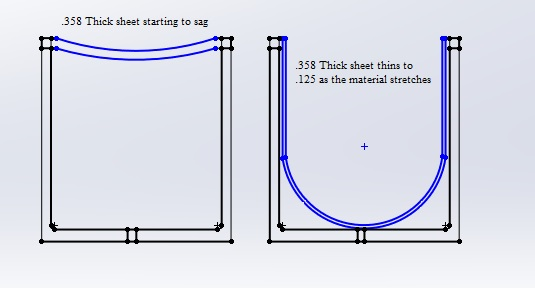
✅ Optimizing Material Distribution:
- Shallow draws (<3:1 draw ratio) are ideal for uniform thickness.
- For deep-draw parts (>3:1 draw ratio), work with engineers to optimize material stretching and prevent thinning.
Enhancing the Aesthetic and Functional Properties of Thermoformed Parts
Surface Finishing and Texturing
Surface finish plays a crucial role in both the appearance and functionality of thermoformed components.
Textured Surfaces: Help to reduce glare, hide fingerprints, and improve grip on functional parts.
Glossy Finishes: Provide high-end aesthetics, commonly used for consumer electronics and display panels.
Silk Screening and Painting: Custom thermoformed parts can be painted, silk-screened, or labeled for branding and usability.
Pro Tip: Many textured materials eliminate the need for post-production finishing, reducing overall costs and improving lead times.
Assembly and Secondary Operations
Thermoformed parts often require additional fabrication for final assembly. Common secondary processes include:
- CNC Trimming & Routing: Precision cutting for holes, slots, and complex shapes.
- Inserts & Fasteners: Molded-in or post-processed fasteners for seamless assembly.
- Heat Staking & Welding: Used to join multiple plastic components together without adhesives.
By planning for secondary operations early in the design phase, engineers can improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
Common Thermoforming Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Even experienced engineers can encounter design challenges when working with custom thermoforming. Here’s how to avoid common pitfalls:
❌ Overly Complex Designs → ✅ Simplify part geometry to improve manufacturability.
❌ Ignoring Draft Angles → ✅ Always include draft for mold release.
❌ Inconsistent Wall Thickness → ✅ Design with uniform material distribution to prevent weak spots.
❌ Selecting the Wrong Material → ✅ Consult with thermoforming experts to choose the best plastic for your needs.
Why Choose CW Thomas for Your Custom Thermoforming Needs?
CW Thomas is a leader in custom thermoforming solutions, offering advanced vacuum forming, pressure forming, and secondary finishing to deliver precision-engineered parts for industries worldwide. With in-house tooling, expert engineering support, and AS9100 and ISO9001-certified quality control, we ensure that every part meets your exact specifications.
Our Custom Thermoforming Capabilities:
✔ In-House Tooling & Engineering – Reducing lead times and improving part consistency.
✔ High-Tolerance Manufacturing – Meeting strict industry standards for medical, aerospace, and industrial applications.
✔ End-to-End Support – From material selection to final assembly, our team ensures seamless production.
Partner with CW Thomas today and optimize your next project with industry-leading custom thermoforming solutions.
Explore more about our custom thermoforming services or contact us for expert consultation.
Elevate Your Custom Thermoforming
By following these best practices in custom thermoforming, engineers and designers can create high-quality, cost-effective, and manufacturable plastic components. From draft angles and material selection to secondary processing and surface finishing, every aspect of thermoforming design impacts performance, durability, and production efficiency.
At CW Thomas, we’re committed to helping clients engineer smarter solutions using precision thermoforming technologies. Contact us today to get started on your next custom thermoforming project.










